Generic S3 plot() and autoplot() (ggplot2) methods to
visualize mlr3 spatiotemporal resampling objects.
Usage
# S3 method for class 'ResamplingSpCVKnndm'
autoplot(
object,
task,
fold_id = NULL,
plot_as_grid = TRUE,
train_color = "#0072B5",
test_color = "#E18727",
repeats_id = NULL,
sample_fold_n = NULL,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'ResamplingRepeatedSpCVKnndm'
autoplot(
object,
task,
fold_id = NULL,
repeats_id = 1,
plot_as_grid = TRUE,
train_color = "#0072B5",
test_color = "#E18727",
sample_fold_n = NULL,
...
)
# S3 method for class 'ResamplingSpCVKnndm'
plot(x, ...)
# S3 method for class 'ResamplingRepeatedSpCVKnndm'
plot(x, ...)Arguments
- object
[Resampling]
mlr3 spatial resampling object of class ResamplingSpCVBlock or ResamplingRepeatedSpCVBlock.- task
[TaskClassifST]/[TaskRegrST]
mlr3 task object.- fold_id
[numeric]
Fold IDs to plot.- plot_as_grid
[logical(1)]
Should a gridded plot using via patchwork be created? IfFALSEa list with of ggplot2 objects is returned. Only applies if a numeric vector is passed to argumentfold_id.- train_color
[character(1)]
The color to use for the training set observations.- test_color
[character(1)]
The color to use for the test set observations.- repeats_id
[numeric]
Repetition ID to plot.- sample_fold_n
[integer]
Number of points in a random sample stratified over partitions. This argument aims to keep file sizes of resulting plots reasonable and reduce overplotting in dense datasets.- ...
Passed to
geom_sf(). Helpful for adjusting point sizes and shapes.- x
[Resampling]
mlr3 spatial resampling object. One of class ResamplingSpCVBuffer, ResamplingSpCVBlock, ResamplingSpCVCoords, ResamplingSpCVEnv.
Details
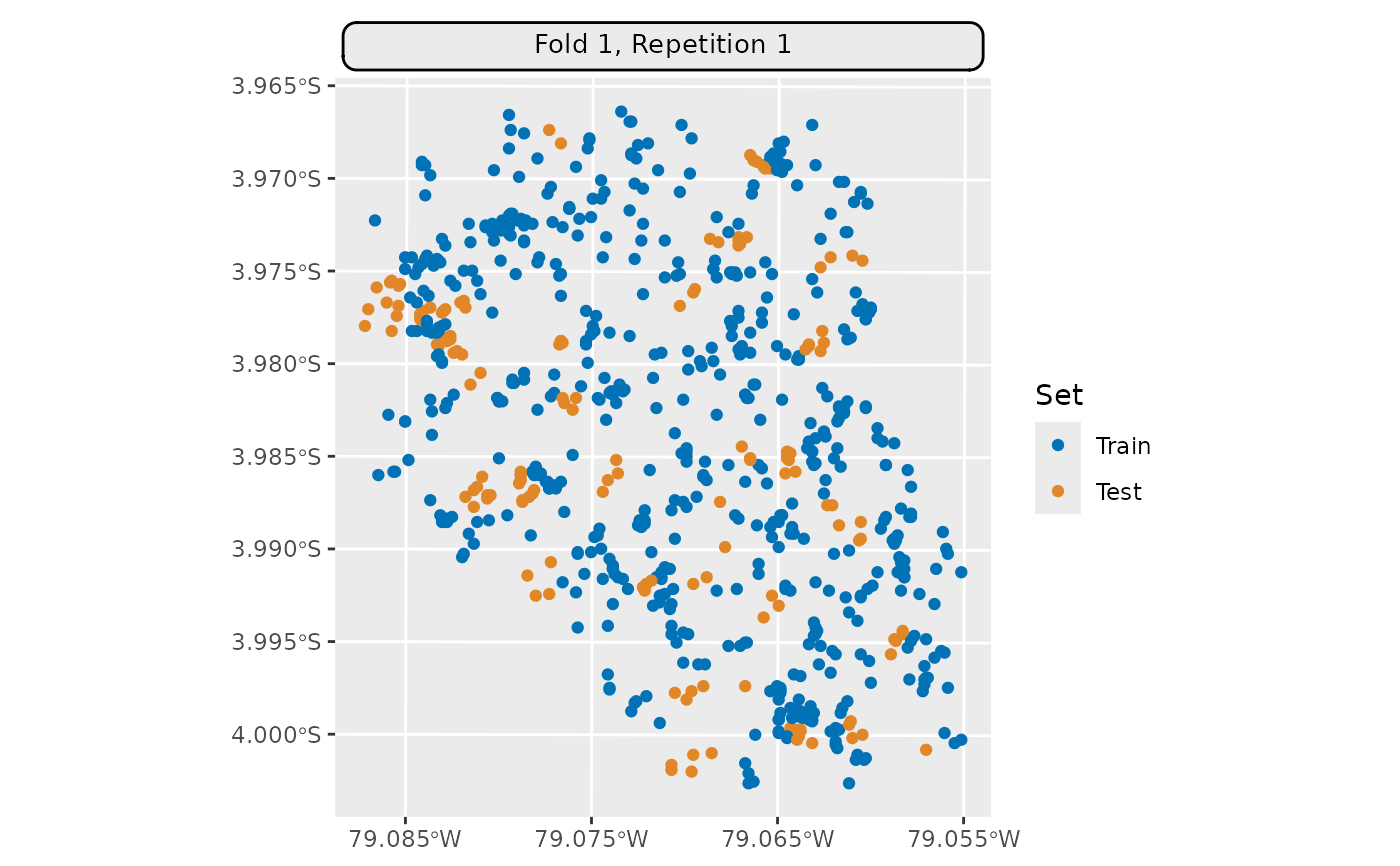
This method requires to set argument fold_id and no plot containing all
partitions can be created. This is because the method does not make use of
all observations but only a subset of them (many observations are left out).
Hence, train and test sets of one fold are not re-used in other folds as in
other methods and plotting these without a train/test indicator would not
make sense.
2D vs 3D plotting
This method has both a 2D and a 3D plotting method.
The 2D method returns a ggplot with x and y axes representing the spatial
coordinates.
The 3D method uses plotly to create an interactive 3D plot.
Set plot3D = TRUE to use the 3D method.
Note that spatiotemporal datasets usually suffer from overplotting in 2D mode.
Examples
# \donttest{
if (mlr3misc::require_namespaces(c("CAST", "sf"), quietly = TRUE)) {
library(mlr3)
library(mlr3spatiotempcv)
task = tsk("ecuador")
points = sf::st_as_sf(task$coordinates(), crs = task$crs, coords = c("x", "y"))
modeldomain = sf::st_as_sfc(sf::st_bbox(points))
resampling = rsmp("spcv_knndm",
folds = 5, modeldomain = modeldomain)
resampling$instantiate(task)
autoplot(resampling, task,
fold_id = 1, size = 0.7) *
ggplot2::scale_x_continuous(breaks = seq(-79.085, -79.055, 0.01))
}
#> 1000 prediction points are sampled from the modeldomain
 # }
# }